Heparin is the anticoagulant of choice when a rapid anticoagulant effect is required because its onset of action is immediate when administered by IV injection. Mechanism of Action.
Heparins Medical Daily News Health News
Mechanism of Action of Heparin.

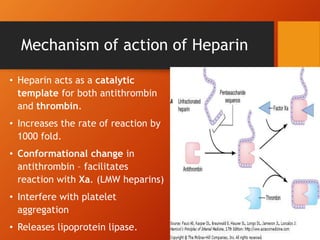
. Heparin also stimulates release of lipoprotein lipase lipoprotein lipase hydrolyzes triglycerides to glycerol and free fatty acids. The mechanism of action is approximately the same for all indications which is to thin the blood and prevent blood clots from forming. The antithrombotic effect of heparin is well correlated to the inhibition of factor Xa.
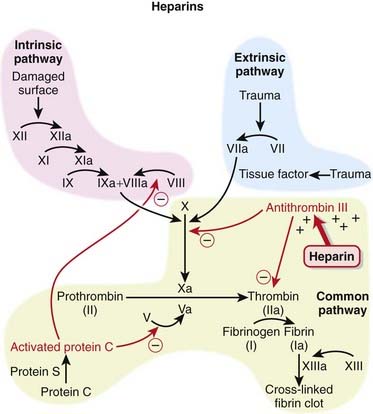
Specifically it is also used in the treatment of heart attacks and unstable angina. It produces its major anticoagulant effect by inactivating thrombin and activated factor X factor Xa through an antithrombin AT-dependent mechanism. This type of drug interferes with the bodys blood clotting process preventing blood clots from forming.
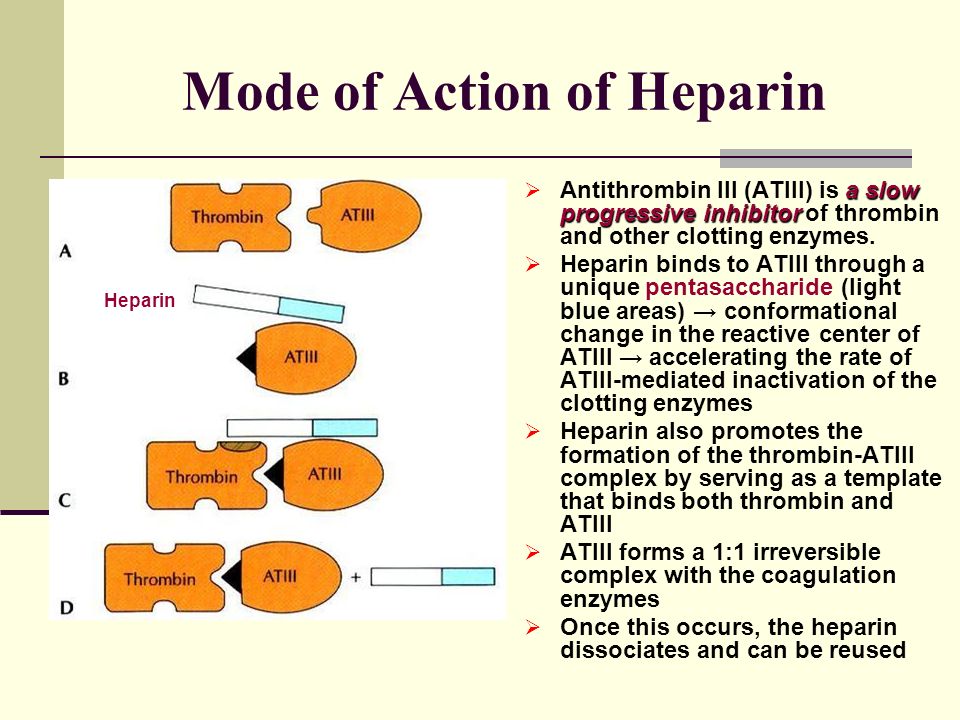
Heparin interacts with the naturally occurring plasma protein Antithrombin III to induce a conformational change which markedly enhances the serine protease activity of Antithrombin III thereby inhibiting the activated coagulation factors involved in the clotting sequence particularly Xa and IIa. SQ use of heparin is used for non-emergent situations. The mechanism by which such high affinity heparin acts when antithrombin III is the inhibitor is promotion of the formation of an intermediate proteinase-heparin-antithrombin complex.
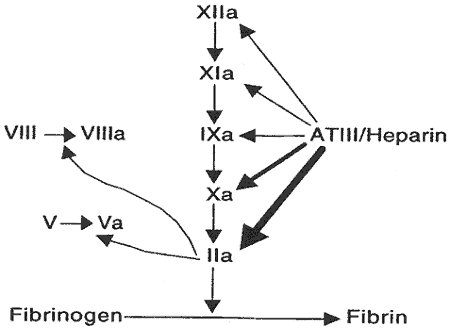
The complex binds to and irreversibly inactivates thrombin and other activated clotting factors such as factors IX X XI and XII thereby preventing the polymerization of. Binding to antithrombin blocks several different factors of the clotting cascade but two are predominant. 25 26 The remaining two thirds has minimal anticoagulant activity at therapeutic concentrations but at concentrations greater than those usually obtained clinically both high- and low-affinity.
Heparin is administered in low doses when used for primary prophylaxis and high doses when used therapeutically to prevent recurrent thrombosis. Heparin mechanism of action. This inhibits the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin and fibrinogen to fibrin.
The requirement for a specific oligosaccharide sequence within. During this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will guide you through the mechanism of action indications adverse drug reactions and contraindications involving heparin. Interaction of hyaluronidase on blood coagulation factors in vitro.
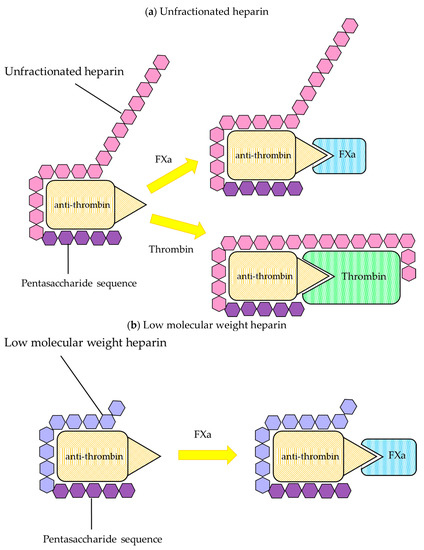
Low Molecular-Weight Heparin LMWH is a heterogeneous collection of heparin molecules with a lower average molecular weight compared to unfractionated heparin. Pharmacology and Mode of Action of Heparin and Glycosaminoglycans Meyer Michel Samama Jeanine M. It acts mainly by accelerating the rate of the neutralization of certain activated coagulation factors by antithrombin but other mechanisms may also be involved.
Heparin is not a thrombolytic or. Pharmacology Mechanism of Action. Join us for our Pharmacology lecture on Heparin.
However it is binding to an antithrombin that is important as this causes a surface change and inactivates thrombin. Monitor signs of allergic reactions and anaphylaxis including pulmonary symptoms tightness in the throat and chest. Its use is usually limited to an in-hospital setting because it must be.
Only approximately one third of an administered dose of heparin binds to AT and this fraction is responsible for most of its anticoagulant effect. The original class Unfractionated Heparin UFH is a crude mixture of variable length polysaccharides derived from porcine intestinal mucosa. Clinico-experimental research on mechanism of action of heparin in rheumatic diseases.
Heparin is administered in low doses when used for primary prophylaxis and high doses when used therapeutically to prevent recurrent thrombosis. Unfractionated heparin UFH binds to anti-thrombin III AT-III which enhances antithrombins inhibition of several coagulation factors especially factor Xa and factor IIa thrombin. Relations between hyaluronidase heparin and salicylates in regard to intradermal diffusion of staining substances.
Heparin also known as unfractionated heparin UFH is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Newer classes known as Low Molecular Weight Heparin LMWH are derived by purification of the smaller molecules within UFH. Low-molecular-weight heparins LMWHs for example dalteparin enoxaparin among others are anticoagulants.
Mechanism Of Action. Heparin is a sulfated polysaccharide with a molecular weight range of 3000 to 30 000 Da mean 15 000 Da. Heparin is sometimes called a.
Notify physician or nursing staff immediately if heparin causes excessive anticoagulation. Download Case Study PDF. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin they are considered anticoagulants.
Heparin inhibits coagulation by activating antithrombin III. Other uses include inside test tubes and. Action Potentiates the inhibitory effect of antithrombin on factor Xa and thrombin.
Heparin is the anticoagulant of choice when a rapid anticoagulant effect is required because its onset of action is immediate when administered by intravenous injection. Once administered heparin binds to several proteins. Heparin is an anti-coagulant drug.
These drugs are used in the prophylaxis of venous thromboembolic disease VTE on acute or elective admission to the hospital and they are used in the treatment of deep vein thromboses DVT and pulmonary embolism PE. Heparin increases the inhibitory action of antithrombin III AT III on clotting factors XIIa XIa IXa Xa and thrombin. Its use is almost always limited to an in-hospital setting because.
Heparin binds to antithrombin III to form a heparin-antithrombin III complex. It also inhibits platelet function. In particular heparin does not appear to have had a significant effect it is very important that a given assay procedure used on the reaction rates between antithrombin III and the in monitoring heparin therapy is understood in terms enzymes preceding factor Xa in the intrinsic pathway of the specific anticoagulant mechanism of action of ie.
Mechanism of Action and Pharmacology of Unfractionated Heparin. Thrombin Factor IIa and Factor Xa. It is given by injection into a vein or under the skin.
Heparin tolerance of the rheumatic subject. Unfractionated heparin UFH came into clinical use in the 1930s making extracorporeal circulation and. Mechanism of action pharmacokinetics dosing considerations monitoring efficacy and safety.
And fall in hematocrit or blood pressure. Potentiates the action of antithrombin III and thereby inactivates thrombin as well as other coagulation factors IXa Xa XIa XIIa and plasmin and prevents the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. Walenga Evi Kalodiki Jawed Fareed Heparin belongs to a class of linear acidic polysaccharides known as glycosaminoglycans GAGs.
Heparin promotion of thrombin inactivation by heparin cofactor II may occur by a similar mechanism. The mechanism of action of heparin is ATIII-dependent.
Mechanisms Of Anticoagulant Drugs Encyclopedia Mdpi

Lecture Notes On Anticoagulants Heparin Warfarin
Heparin Physiology Pharmacology And Clinical Application
Anticoagulant Therapy Ppt Download

Anticoagulants Hematology Medbullets Step 1

Mechanism Of Action Of Heparin A In The Absence Of Heparin Download Scientific Diagram

Heparin Mechanisms Within The Coagulation Cascade Box A At Red Download Scientific Diagram
Heparin Physiology Pharmacology And Clinical Application

Pharmacological And Clinical Application Of Heparin Progress An Essential Drug For Modern Medicine Sciencedirect

Mechanisms Of Action Of The Different Thrombin Inhibitors A The Download Scientific Diagram

Heparin Mechanism Of Action Study Com

Heparin And Low Molecular Weight Heparin Mechanisms Of Action Pharmacokinetics Dosing Monitoring Efficacy And Safety Chest

Mechanism Of Action Of Unfractionated And Low Molecular Weight Heparin Download Scientific Diagram

Heparin Mechanism Of Action Youtube

Anticoagulants Heparin Osmosis

Pdf Mechanisms Of Action Of Low Molecular Weight Heparins And Heparinoids Semantic Scholar